The story of our national parks is also a remarkable story of resilience and collaboration in hard times. Just as the national parks were becoming popular, the Depression brought unprecedented unemployment and bare scarcities at home, on the farm, and in cities. Leaders with optimistic vision were challenged to engage an illiterate and unskilled workforce or face severe cultural, social, and economic consequences.
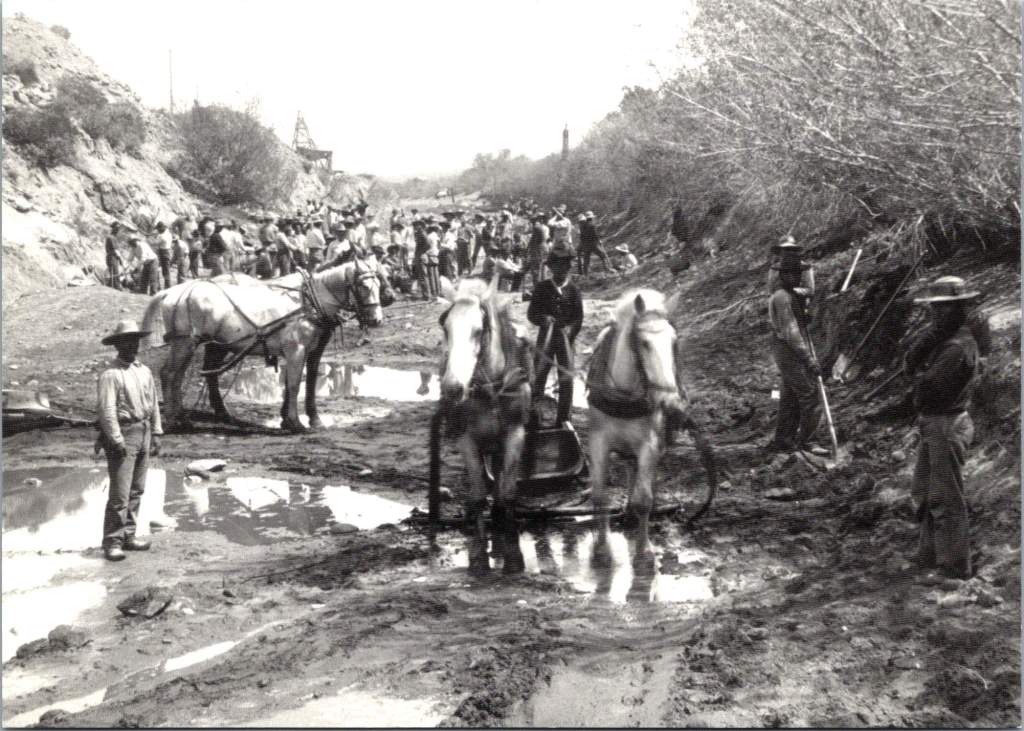
The Civilian Conservation Corps’ work in Yellowstone exemplified an unprecedented partnership between federal agencies, orchestrated by a remarkable team. Robert Fechner, the program’s first director, brought his labor union experience to balance competing interests that might have limited the program. Harold Ickes, as Secretary of the Interior, ensured high standards for conservation work. The Department of Labor selected the men for service in the corps. The Army constructed and operated the camps. The National Park Service and Forest Service supervised the technical and construction work. This complex dance of bureaucracy somehow produced remarkable efficiency, with the CCC completing projects that had languished on drawing boards for decades.

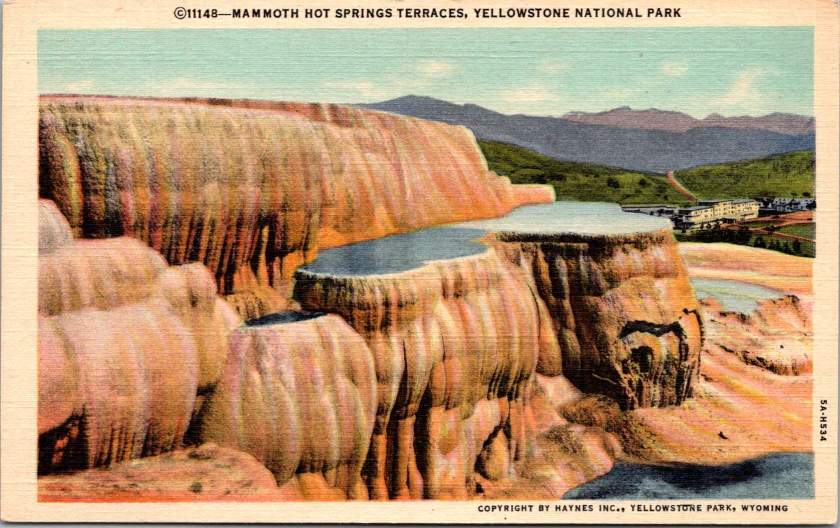
Take the terraced formations of Mammoth Hot Springs, for example, their delicate travertine steps descending the hillside in nature’s own architecture. CCC workers constructed the stone steps and walkways that would allow visitors to safely view these natural wonders. The careful integration of human infrastructure with natural features became a hallmark of CCC work. Now known as ‘parkitecture’, the philosophy would influence park design for generations.
Long before the federal programs, Frances Perkins coordinated closely with Roosevelt during his New York state governorship to protect workers and grow the workforce. She had witnessed the Triangle Shirtwaist Factory fire in 1911, an experience that drove her lifelong commitment to worker safety and labor reform. As New York’s Industrial Commissioner from 1929 to 1933, Perkins pioneered unemployment relief programs and worker protections that would later shape New Deal policies. When Roosevelt became president, he named her Secretary of Labor – the first woman to serve in a presidential cabinet – and she brought her New York experiences to Washington just in time.
Perkins understood the value of both job creation and job training, having seen their impact in New York. She helped shape the CCC, carefully navigating the political tensions around women’s employment programs. Her influence helped ensure that CCC and other programs included educational components, reflecting her belief that economic relief should build long-term capabilities, not just provide temporary aid. She also made sure the federal programs benefited her home state, and piloted important new programs there.

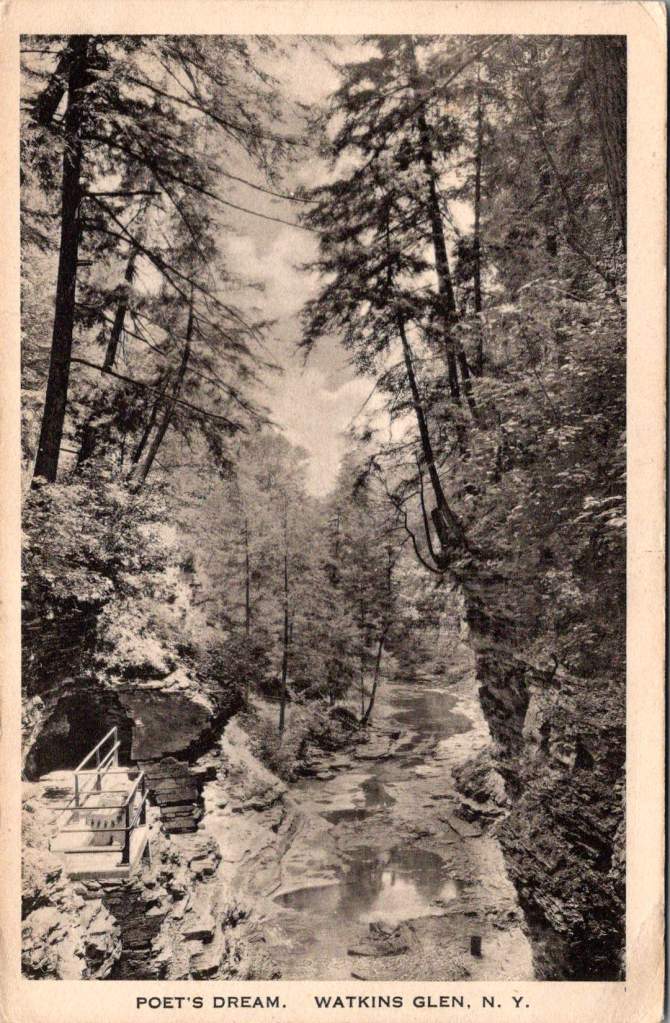
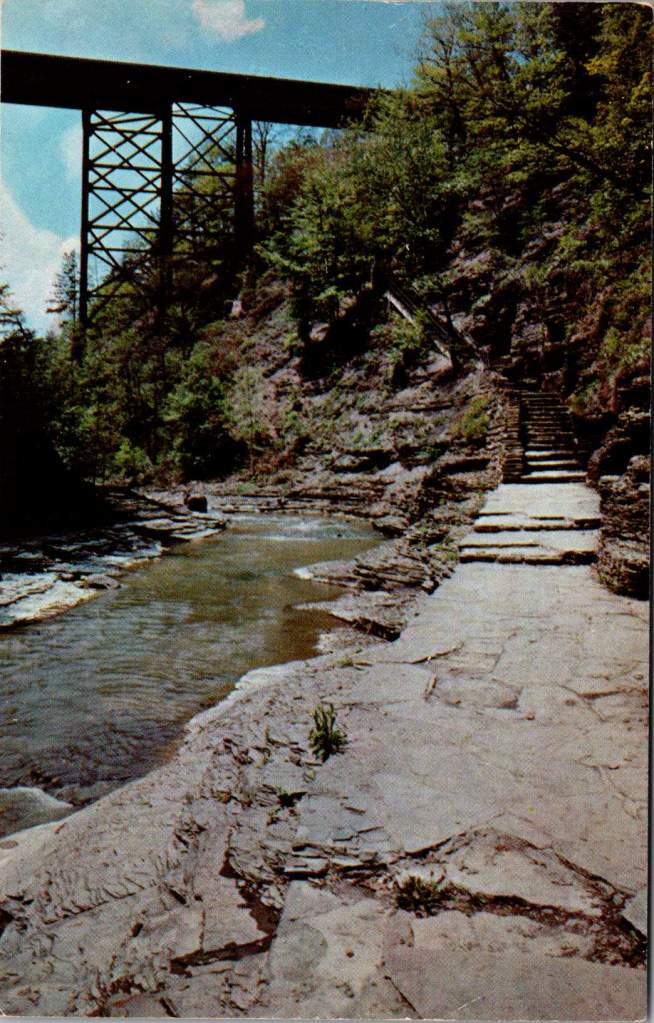
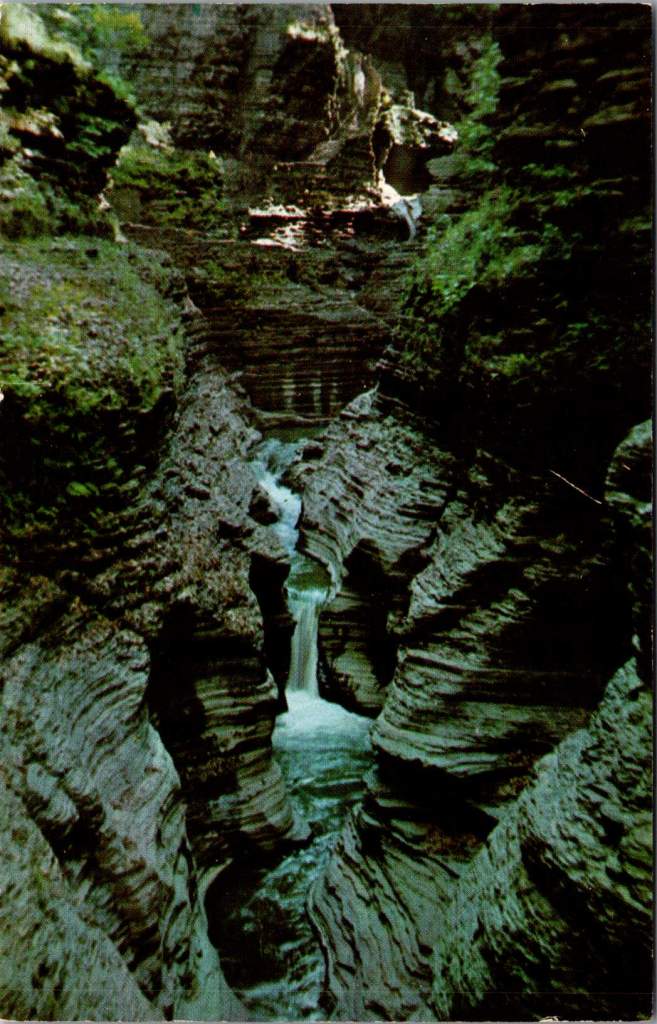
A 1905 hand-colored postcard of Watkins Glen in New York state shows Diamond Falls in the distance, framed by the narrow gorge’s layered rock walls. When the CCC arrived here in the 1930s, they found a park already famous for its natural beauty but in need of significant infrastructure. The Corps constructed the stone walkways that still guide visitors through the glen today, built overlooks at strategic points, and created a trail system that made the park’s dramatic features accessible while preserving their natural character.

The CCC’s work at Watkins Glen was particularly challenging given the varied landscape and unique natural formations. Jacob’s Ladder, a daunting stone staircase ascending the gorge wall, required precise engineering to integrate it naturally into the rock face. The Corps workers quarried stone and shaped the ascent, creating a path that appear to emerge organically from the cliff itself.

At Rainbow Falls, they constructed the “flying stairs” – suspended pathways that seem to float alongside the cascading water. This required not just skilled stonework but innovative engineering to ensure the structures could withstand the gorge’s frequent flooding and harsh winters. The Stairway to Lover’s Lane presented similar challenges, with workers having to carefully cut into the gorge wall while preserving its natural beauty.

The Corps also built the park’s amphitheater, transforming a natural hollow into a gathering space that would host generations of visitors for educational programs. Throughout these projects, workers had to move tons of stone while working in the confined space of the gorge. They developed specialized techniques for working in the narrow spaces, often suspended above the creek as they built pathways that had to withstand both regular flooding and freezing temperatures. The project showcased the Corps’ ability to combine heavy construction with delicate environmental consideration – skills that would prove valuable throughout the park system.
Yet while young men were building parks across America, another story was unfolding at Bear Mountain, New York. A smaller program called the Temporary Emergency Relief Administration (TERA) – nicknamed the She-She-She camps – was offering women their own opportunity for training and education. Eleanor Roosevelt championed this effort, collaborating closely with progressive educator Hilda Worthington Smith to create a program that emphasized both practical skills and broader education.

At Camp TERA, women learned furniture refinishing, bookbinding, typing, and business skills. They studied literature, current events, and public speaking. The curriculum reflected both practical needs and progressive educational ideals, emphasizing peer learning and leadership development. The camps created a college-like atmosphere, quite different from the military structure of CCC camps.

The economics of these programs tell their own story. Spending roughly $1,000 per enrollee annually (about $25,000 in today’s dollars) the CCC cost $3 billion over nine years – equivalent to about $60 billion today. In its time, the program returned an estimated $2.50 in measurable public benefits for every dollar spent. Each CCC enrollee earned $30 monthly, with $25 sent home to their families – enough to keep many families fed during the Depression’s darkest days. The TERA budget was much less and never achieved the scale that made the CCC so cost-effective, yet for some of the women who participated, the return on investment was significant in improving their health, caregiving capacities, and professional skill sets – many went on to careers in business, education, and public service.
The CCC employed three million men over nine years. TERA participants numbered just 8,500 women. Despite Eleanor Roosevelt’s advocacy and Frances Perkins’ support from the Labor Department, the women’s program expanded only briefly and never really got off the ground. The reasons echo familiar themes: limited funding, resistance to women working outside the home, and debates about appropriate roles for women in society.
These limitations weren’t unique to TERA. The CCC itself reflected America’s racial divisions, with segregated camps and discriminatory selection. Some local communities opposed Black CCC camps in their areas. The program’s focus on young, single men also excluded many who needed help.

Yet for all their limitations, the New Deal’s public works programs transformed America’s public spaces. Beyond the CCC and TERA, the Works Progress Administration built parks, schools, and community centers nationwide. WPA artists created murals that still enliven post offices and courthouses today. Collectively, WPA workers built communities, developed national infrastructure, and documented American life through photography and collected folk songs and stories that might otherwise have been lost.
The human legacy of these programs extends far beyond their physical achievements. Chuck Yeager, the pilot who would later break the sound barrier, learned mechanics in the CCC. Stan Musial developed his work ethic in a Pennsylvania CCC camp before becoming a baseball legend. Robert Mitchum and Raymond Burr worked in CCC camps before their Hollywood careers. From the TERA camps emerged teachers, business leaders, and community organizers who shaped their communities for decades to come.



Looking at these vintage postcards today, we can measure the value of these programs not just in the enduring infrastructure they created, but in the generational impact of providing education and opportunity to millions of Americans of modest means. Think of the families fed by CCC wages, the skills learned, the confidence built. Consider the children and grandchildren who grew up hearing stories of carving out Yellowstone’s trails or getting the chance to study at Bear Mountain, who inherited not just the physical legacy of these programs but their spirit of public service and possibility. Think of all of us today, who still climb the steps and set our sights on this same legacy.




The trails around Old Faithful, the stone steps at Watkins Glen, the walkways at Mammoth Hot Springs – all have weathered nearly ninety years now, crossed by millions of visitors. They stand as monuments not just to American craftsmanship, collaboration, and ingenuity but to the transformative power of public investment in both our spaces and our people. They give us examples of leadership and also remind us of the great many unknown men and women who preserved and protected the places we love. Their endurance challenges us to imagine what might be achieved in this generation if we again dared to think so boldly about developing our natural resources and our human potential together.