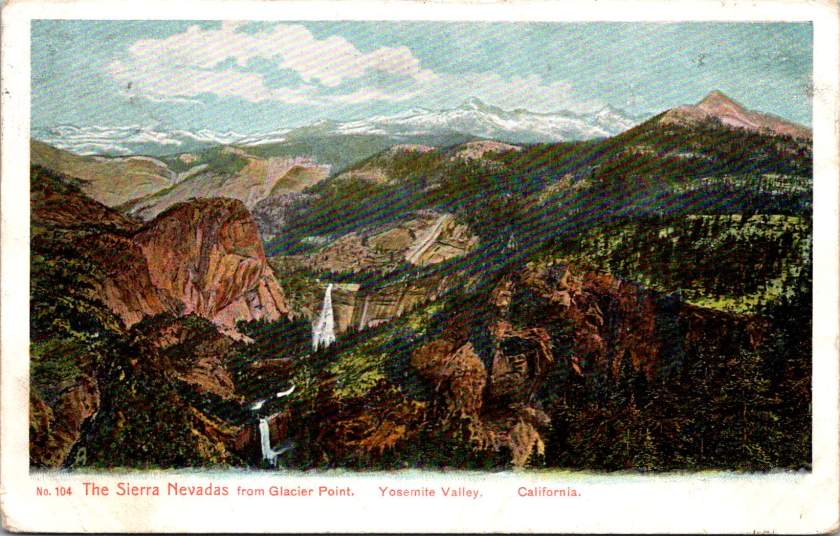
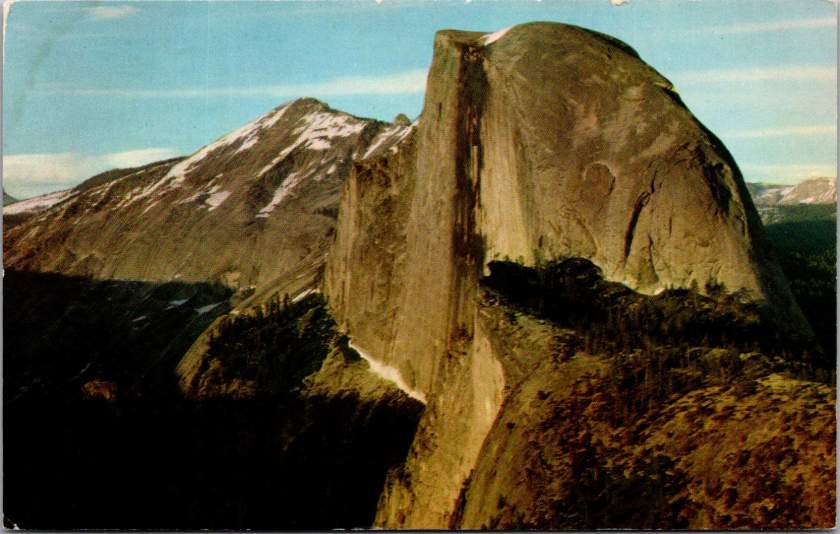
When Abraham Lincoln signed legislation in 1864 protecting Yosemite Valley, few Americans had seen its wonders firsthand. The journey was arduous, expensive, and often dangerous. But photographs and artistic renderings began circulating, capturing public imagination. Carleton Watkins’ mammoth plate photographs of Yosemite’s towering cliffs and Albert Bierstadt’s luminous paintings suggested something almost mythical: a uniquely American paradise, waiting to be experienced.
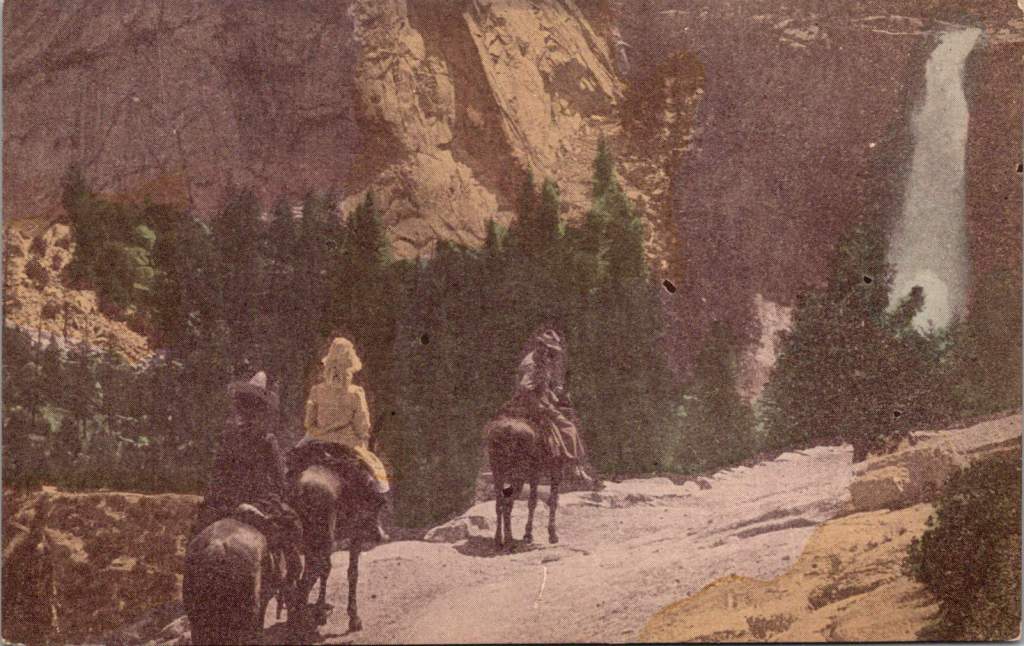
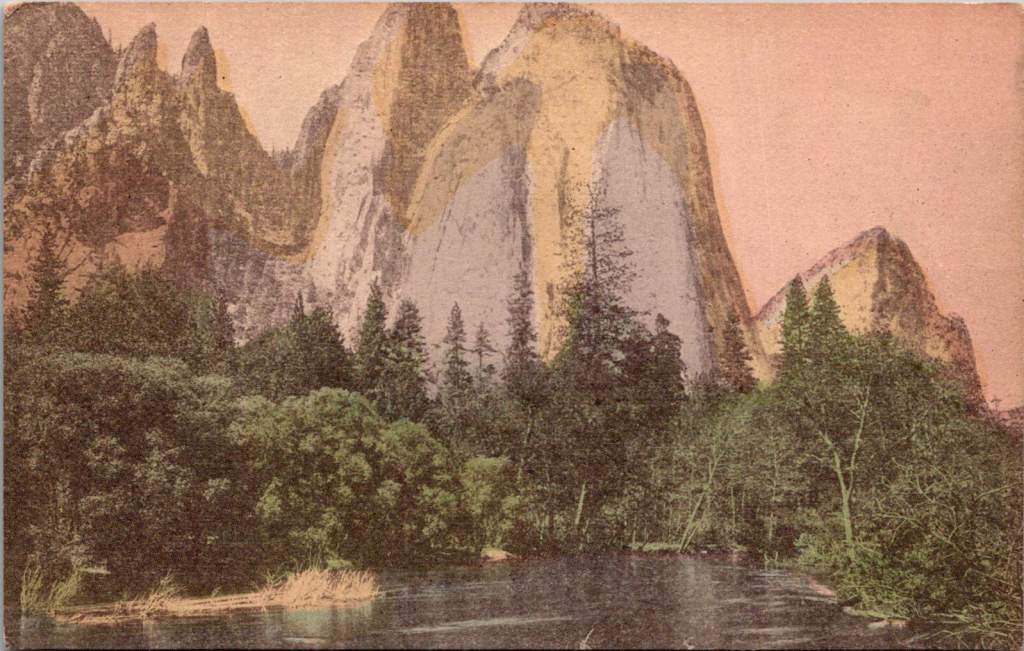




By the 1880s, the Southern Pacific Railroad had begun marketing Yosemite as a must-see destination. Their promotional materials featured romantic images of pristine wilderness alongside luxury dining cars and comfortable accommodations. The message was clear: you could experience the sublime while maintaining the comforts of civilization. The railroad’s campaign to “See America First” tapped into both patriotic sentiment and growing concern about wealthy Americans choosing European vacations over domestic travel.
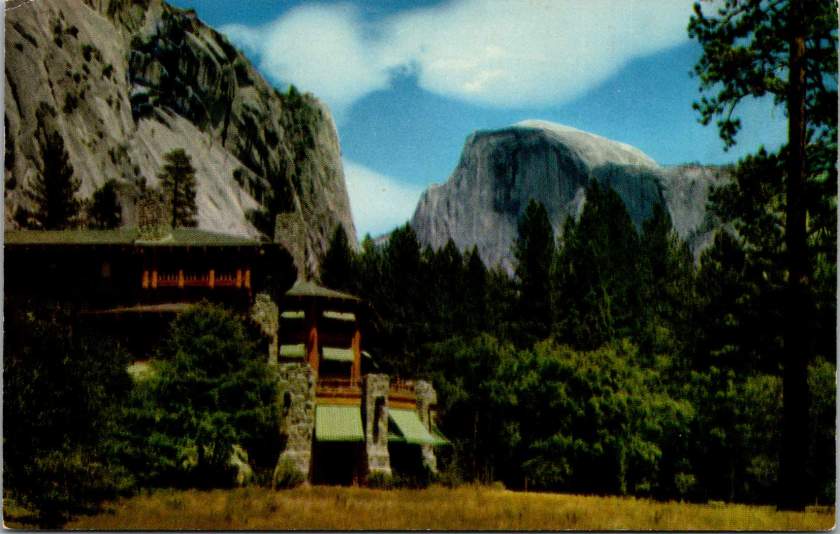
Stephen Mather, who would become the first director of the National Park Service in 1916, understood the power of imagery. A self-made millionaire from the borax industry, he approached park promotion with a marketer’s eye. Mather encouraged photographers to set up studios in Yosemite and actively supported the production of high-quality postcards, which he called his “little missionaries.” These cards, purchased for pennies and mailed across the country, did more than any official campaign to make Yosemite a part of the American imagination.
The postcards reveal changing patterns in how Americans experienced their parks. Early images show well-dressed visitors on guided tours, often on horseback. By the 1920s, automobiles appear, marking a democratic shift in park access. The famous Wawona Tree tunnel, carved through a giant sequoia in 1881, became a must-have photo opportunity. Each car passing through represented a family making their own way through the park, free to explore at their own pace.
The National Park Service itself emerged from a uniquely American compromise. Progressive Era conservationists like John Muir had argued for pure preservation, while others saw the parks as natural resources to be utilized. The 1916 Organic Act that created the NPS threaded this needle by mandating both conservation and public access – the parks would be preserved unimpaired, but explicitly for the enjoyment of the people.
This dual mandate shaped how Americans came to view their relationship with nature. The parks weren’t distant wilderness to be admired from afar, but rather public spaces to be actively experienced. In the 1930s Civilian Conservation Corps workers built trails and facilities, making the parks more accessible while maintaining their natural character. The message was clear: these were the people’s parks, and the people would help maintain them.
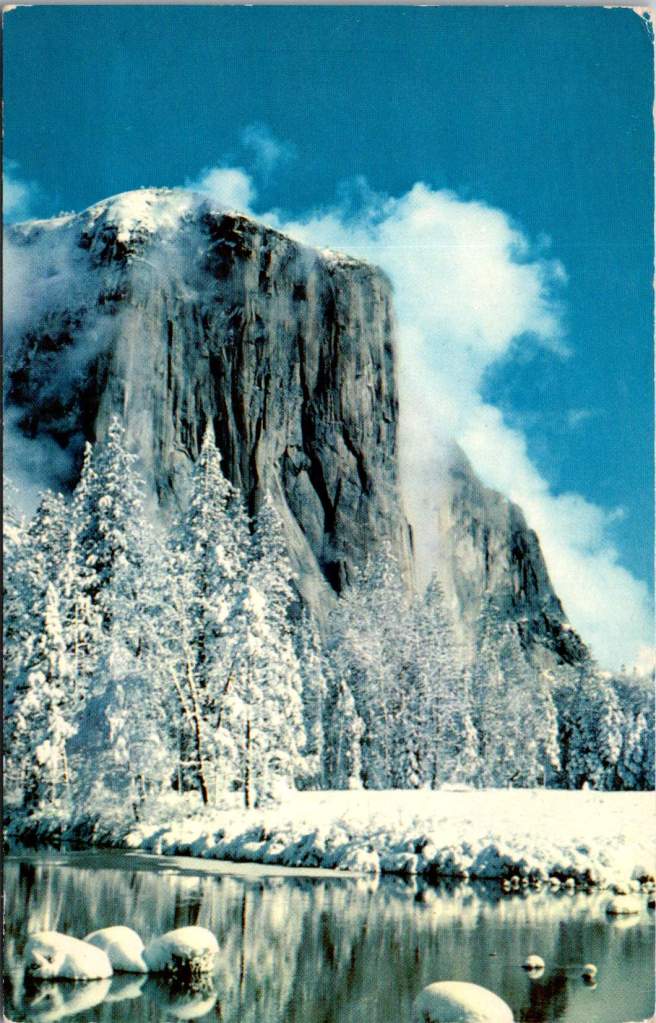
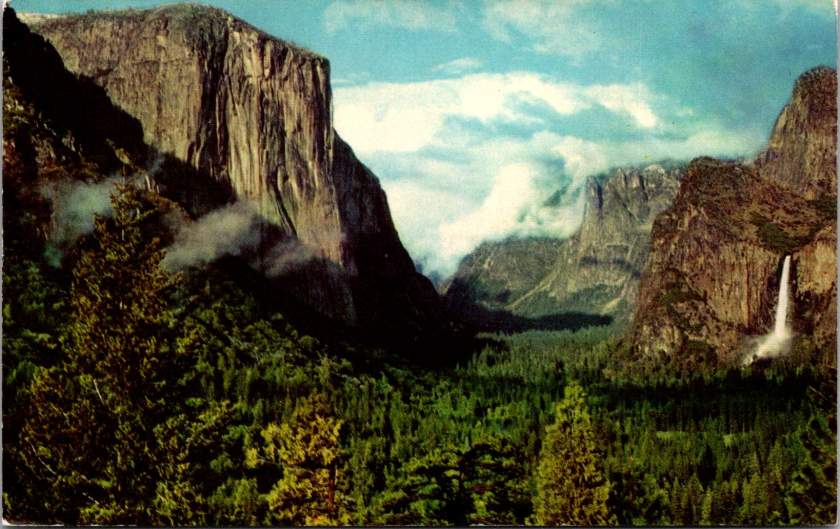
The advent of color photography in the 1940s and 50s brought new vibrancy to park imagery. Postcards from this era capture the brilliant white of dogwood blooms along mountain streams, the deep red of sequoia bark, and the rainbow mist of Yosemite Falls. The images suggested that black and white photography, no matter how artistic, had never quite captured the true glory of these places.
By the mid-20th century, the success of the national parks as tourist destinations began creating new challenges. Bumper-to-bumper traffic in Yosemite Valley became an ironic commentary on Americans’ enthusiasm for their natural heritage. The park service faced growing tension between access and preservation, leading to innovations like shuttle systems and visitor quotas.
Yet the fundamental appeal of the parks remained unchanged. Whether arriving by horse, train, automobile, or tour bus, visitors came seeking what Frederick Law Olmsted had described in his 1865 report on Yosemite, “The union of the deepest sublimity with the deepest beauty of nature.” The parks offered not just scenic views but a connection to something larger than themselves – a uniquely American inheritance.
Today’s visitors to Yosemite might share their experiences through Instagram rather than postcards, but they’re participating in the same tradition of witnessing and sharing America’s natural wonders. The early promoters of the national parks understood something fundamental: seeing these places wasn’t enough. The experience had to be shared to become part of our collective identity.
Those early postcards, with their hand-tinted colors and earnest captions, did more than advertise scenic views. They helped Americans understand these distant wonders as their own inheritance – places that belonged to everyone and therefore needed everyone’s protection. When we look at them today, we’re seeing how Americans fell in love with their national parks, and how that love affair helped define our relationship with the natural world.

The history of Yosemite and the National Park Service reminds us that conservation isn’t just about preserving scenic views. It’s about maintaining spaces where each generation can discover their own connection to the natural world. This fundamental mission remains as relevant as ever. The parks still offer what those early postcards promised: a chance to see the natural wonders of the United States, and to share the experience with friends and family miles away.