The postcard is colorful, smartly-designed and professionally printed, but it’s not a scenic view or a greeting from a distant relative. It’s a fold-over commercial mailer. Inside is a detailed cattle market report from Woodson-Fennewald Company at the National Stock Yards in Illinois.
For rural farmers and ranchers like Van Hooven, this small mailed card represented opportunity and prosperity. Today, it’s a window into a complex economic ecosystem that stretches from a small ranch in eastern central Missouri to the bustling stockyards of Chicago and beyond. This postcard and another one received a decade later bookend a period of dramatic change in rural America.


Van Hooven’s address in Americus draws us to a small community in in the eastern central part of Missouri. Founded in the 1860s Americus grew from a pre-Civil War settlement into a bustling village. By 1884, it boasted a dry goods store, a drug store, two blacksmith shops, a wagon shop, and a steam-powered saw and grist mill.
The town’s very existence was cemented when it gained its own post office, initially called Dry Fork Mills before town residents objected. The nobly-named Americus post office was a vital link to the outside world, enabling the flow of information that savvy rural ranchers relied on.
Van Hooven’s property likely sat in a landscape perfectly suited for a variety of livestock and farming operations. Nestled in the rolling hills near the Loutre River, his land would have been a patchwork of forests, streams, and fertile valleys. In this varied terrain, he may have run a sizable cattle herd while also providing habitat for a variety of wildlife – a fact that will prove crucial in the years to come.
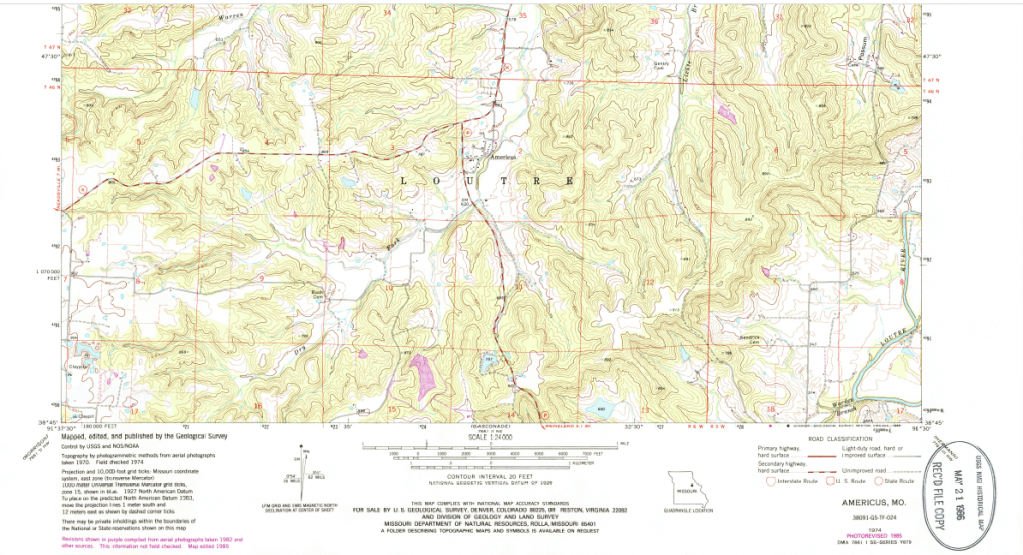
A topographic map from 1974 shows this diverse landscape. Americus sits in a relatively flat area surrounded by hills, with numerous streams creating a dendritic pattern, like branching trees across the region. It’s easy to imagine cattle grazing in the lush river bottoms, while the forested hills provide shelter and resources.
Roaring Twenties on the Ranch
As Van Hooven studied the 1926 cattle prices, perhaps he was feeling his good fortune. The Roaring Twenties were in full swing, and the prosperity had reached even small towns like Americus. If he had invested in quality breeding stock, those “choice light weight steers and yearlings” were commanding premium prices. If he also had hogs and sheep, the the Woodson-Fennewald report would have mattered even more.
The postcard hints at the changing nature of transportation: “Good roads and bigger trucks” are increasing business. Maybe he should buy a truck? Despite the postcard’s offer, he could bypass middlemen and transport his cattle directly to the stockyards, increasing his profits.
This era of prosperity had allowed rural entrepreneurs to expand operations, explore new sources of revenue, and adopt new trades. Van Hooven and those like him were in a rapidly changing economic climate, keenly attuned to market forces. Subscribing to agricultural journals and almanacs, attending county fairs, and experimenting with new breeds of cattle would improve herd quality and potentially one’s livelihood.
As the 1920s progress, many rural farms and ranches began to feel the pinch of falling agricultural prices. The postwar boom that had inflated crop and livestock prices was ending, and rural people struggled with debt taken on during the good years.
Then came the stock market crash of 1929, sending shockwaves through the American economy. Rural communities like Americus were hit hard. Cattle prices plummet, and many farmers found themselves unable to make mortgage payments on land and equipment.
A conservative approach and diverse operations may have insulated ranching operations somewhat. But if not himself, Fred Van Hooven certainly would have seen his neighbors begin to struggle.


Rural Adaptation and Survival
Fast forward to a frosty January morning in 1936. Van Hooven, now a decade older and wiser, shuffled through his mail. Another postcard caught his eye, this one from David Blustein & Bro. in New York City. It’s a detailed price list for animal furs. Wolf pelts were fetching $8 for large, prime specimens, while muskrats, abundant in the streams around Americus, are listed at $1.40 for the best quality.
As the Great Depression deepens, Van Hooven’s adaptability must come to the fore. Years of reports and price lists have taught him to read the markets. While his cattle operation suffered, he must have looked for other opportunities.
The forests and streams around Americus, once seen mainly as grazing land, now represent a different kind of potential. Farmers and ranchers could supplement their income through trapping, a grueling work that involves checking traplines in the freezing pre-dawn hours. Van Hooven may have learned from older members of the community, who remembered the days when fur trading was a major part of Missouri’s economy.
For everyone in Americus, successful adaptation to the harsh realities of the Depression was required in one way or another. Expert trappers built upon older trapping techniques and learned how to properly prepare and grade furs to fetch the best prices. Chilled railcars brought the trade back for a while and made way for greater livestock shipping, too. The Blustein postcard listed nine different animal furs, each with three grade levels. Mink, marten, and beaver commanded the highest prices, but even the humble muskrat and possum contributed to the bottom line.
Changing Economic Ecosystems
Both postcards – the 1926 cattle report and the 1936 fur price list – highlight the surprisingly global nature of rural commerce in early 20th century America. From his small farm in central Missouri, Van Hooven was connected to markets in Chicago, New York, and beyond. The prices he received for his cattle or furs were influenced by national and international demand, linking the economy of Americus to the broader world.
This interconnectedness was facilitated by a complex communications network. Regular market reports and price lists delivered by mail kept rural entrepreneurs informed of distant market conditions. The level of detail in these reports – from specific cattle grades to fur sizes – shows the sophistication expected of ranchers, farmers and trappers.
The story behind these postcards is more than just a tale of one farmer’s adaptability woven out of the clues we have here. It’s a testament to the resilience and entrepreneurial spirit that has long characterized rural America. We would have to do more genealogical research to truly understand Fred Van Hooven’s story. For us, his name and address is just a place to start.
But we can assume that Van Hooven faced some of the same challenges confronting rural communities today. He would have had to navigate the boom of the 1920s and the bust of the 1930s. Van Hooven’s move from solely cattle ranching to include fur trapping highlights the ongoing need for rural businesses to diversify and adapt to changing markets. The shift from rail to road transport in Van Hooven’s time echoes the digital revolution of today, presenting both challenges and opportunities for rural businesses.
The postcards show how even in the 1920s and 1930s, rural businesses were connected to global markets. Today’s rural entrepreneurs face a rapidly changing economic landscape, from globalized markets to the impacts of climate change.

Enduring Spirit in Rural America
Today, Americus still appears on maps, a testament to the enduring spirit of rural communities. While fur trading and lone cattle drives have largely faded into history, the legacy of adaptability and connection to broader markets lives on. Modern farmers and rural entrepreneurs face their own set of challenges, but they approach these obstacles with the same resilience and ingenuity that characterized prior generations.
The humble business postcards that once delivered vital market information have been replaced by smartphones and real-time digital updates. Yet the essential skills they represent – market awareness, adaptability, and entrepreneurial spirit – remain as crucial as ever for rural success.
As we face the economic uncertainties ahead, let’s remember the lessons embodied in these postal relics. Rural America has always been a place of innovation and resilience where hard work and adaptability can turn challenges into opportunities. Next time you pass through a small Midwestern town, remember the papers and pricing that was once news traveling from the nation’s bustling cities to quiet rural routes – and consider how those connections continue to evolve and shape rural life today.
Discover more from The Posted Past
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
