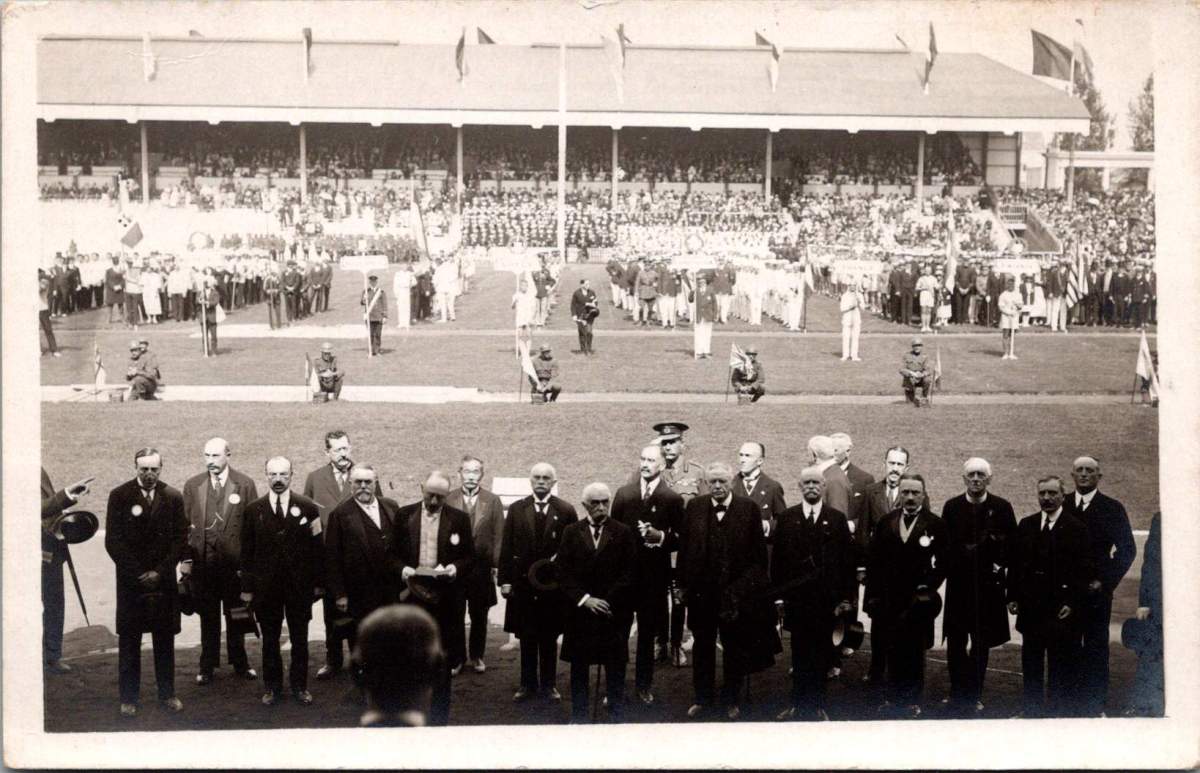
At first glance, it might seem like just another black-and-white snapshot of a bygone event. But look closer, and you’ll find yourself face to face with influential figures of the early 20th century. General John J. Pershing, commander of the American Expeditionary Forces during World War I, is captured in a crisp military salute. Baron Pierre de Coubertin, the father of the modern Olympic movement, instantly recognizable by his distinctive mustache.
This single frame tells a story far greater than the sum of its parts. Shot by an unknown photographer and made into a real photo postcard by Thomas Illingworth & Co., it shows a world emerging from the shadows of war and pandemic.
A week earlier, US women won the vote and swimmer Ethelda Bleibtrey was about to bring home gold. The greats of the era – Duke Kahanamoku, Suzanne Lenglen, Paavo Nurmi, Frank Foss, and 72-year old Oscar Swahn – embodied the world’s tenuous progress through their excellence and effort in sport.
The accompanying 17 photos show the Parade of Athletes, including Australia, Belgium, Canada, Denmark, Egypt, France, Greece, Italy, Japan, Norway, South Africa, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, and USA. Each delegation presented themselves to the Belgian King, sometimes with a wave or salute.






Window into 1920
Before we dive into the significance of the individuals captured in this image, let’s consider the medium itself. In 1920, the postcard was more than just a souvenir; it was a vital means of communication and a bearer of visual stories in a pre-digital age.
The postcards we’re examining used light-sensitive paper, a recently available technology in the marketplace. In this case, the Horse Shoe Brand from Thomas Illingworth & Co. – tells us exactly who produced the photographic prints directly from negatives. Each card, despite being a reproduction, was essentially a unique photograph, carrying subtle variations in exposure and tone that mass-printed cards could never match.
The quality of these postcards was remarkable for their time. The ability to clearly discern General Pershing’s salute and the details of de Coubertin’s mustache over a century later is a testament to the craftsmanship involved in their production. It’s also a stroke of luck for historians, providing us with invaluable visual evidence of this pivotal moment in Olympic history.
A General’s Salute: More Than a Gesture
The presence of General John J. Pershing at the 1920 Antwerp Olympics, captured mid-salute, is laden with symbolism. Just two years earlier, Pershing had been commanding millions of troops in the bloody fields of Europe. Now, here he was, saluting not to the drums of war, but to the peaceful competition of nations. The crowd was thrilled when Belgian soldiers released doves of peace to open the ceremonies.
Pershing’s salute was a powerful endorsement of the Olympic movement’s ideals, and a gesture of solidarity to the King of Belgium, who he is facing in the stands. It’s a military man’s acknowledgement that the battlefield is not the only place where nations can meet. The attendance of the two military commanders lent gravitas to the event, underlining the Games’ importance in post-war international relations.
Moreover, Pershing’s attendance highlighted the changing role of the United States on the world stage. The U.S. had emerged from World War I as a major global power, and Pershing’s presence at the Olympics signified America’s commitment to engaging with the international community not just through politics and economics, but through culture and sport as well.
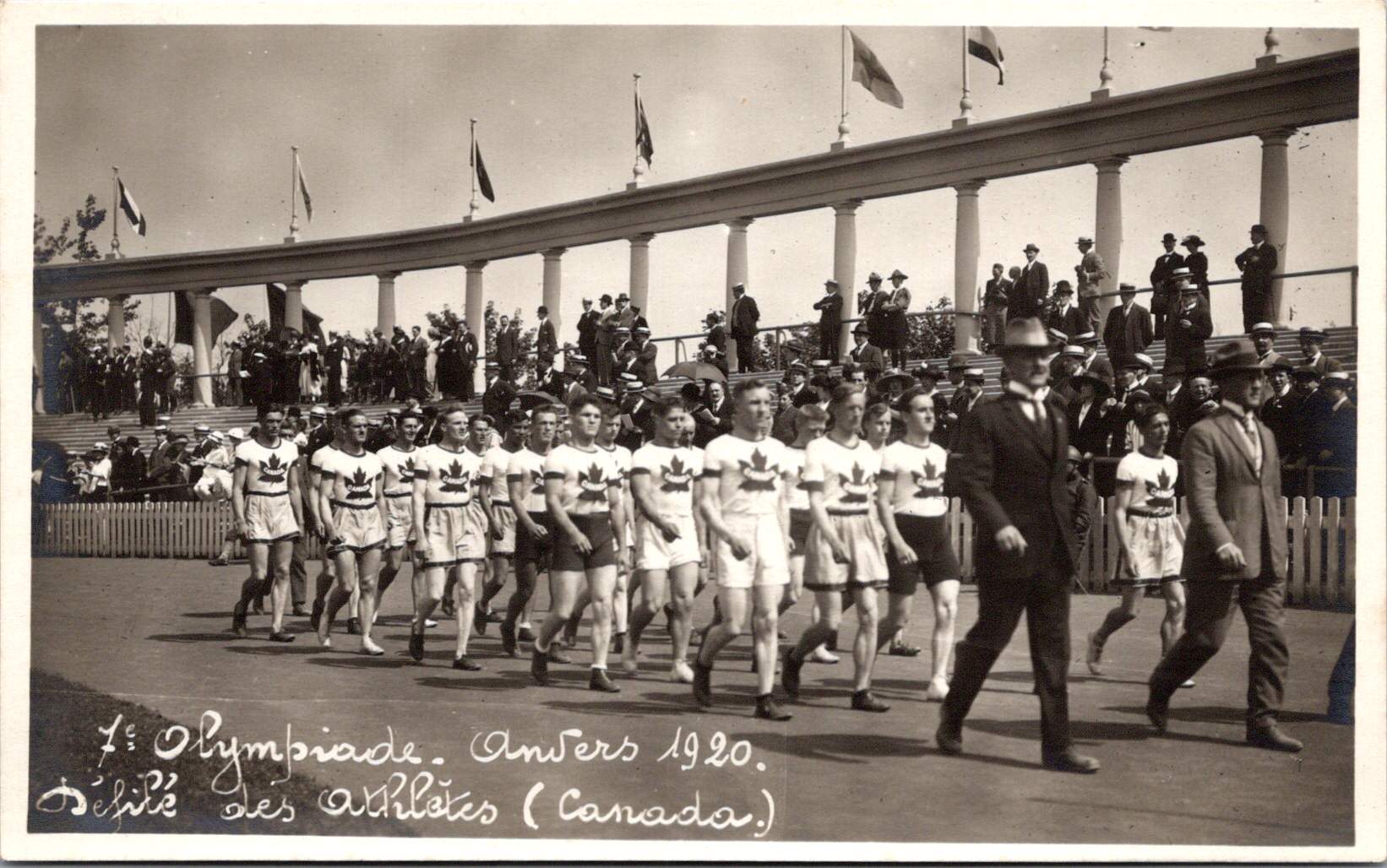
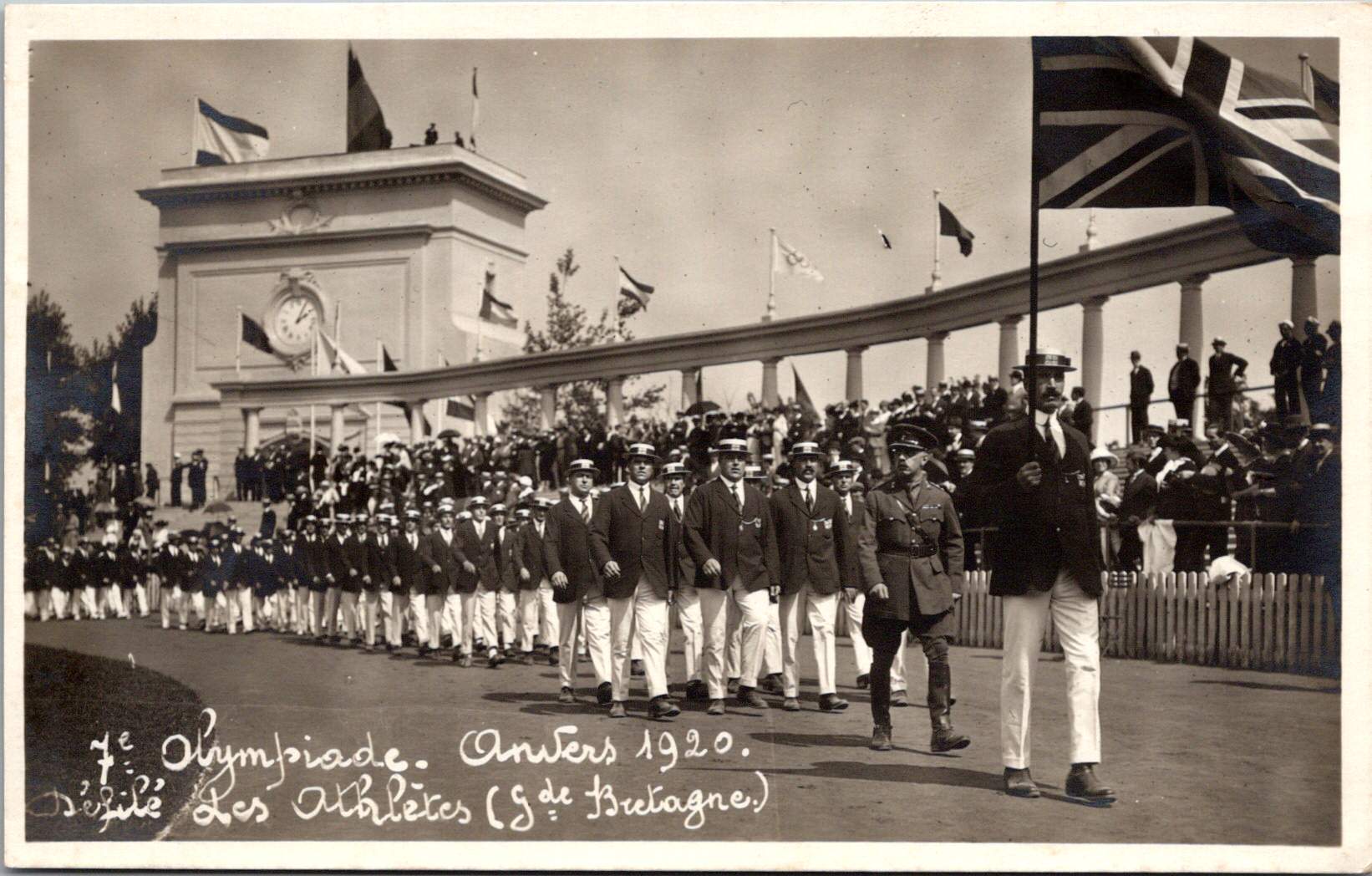
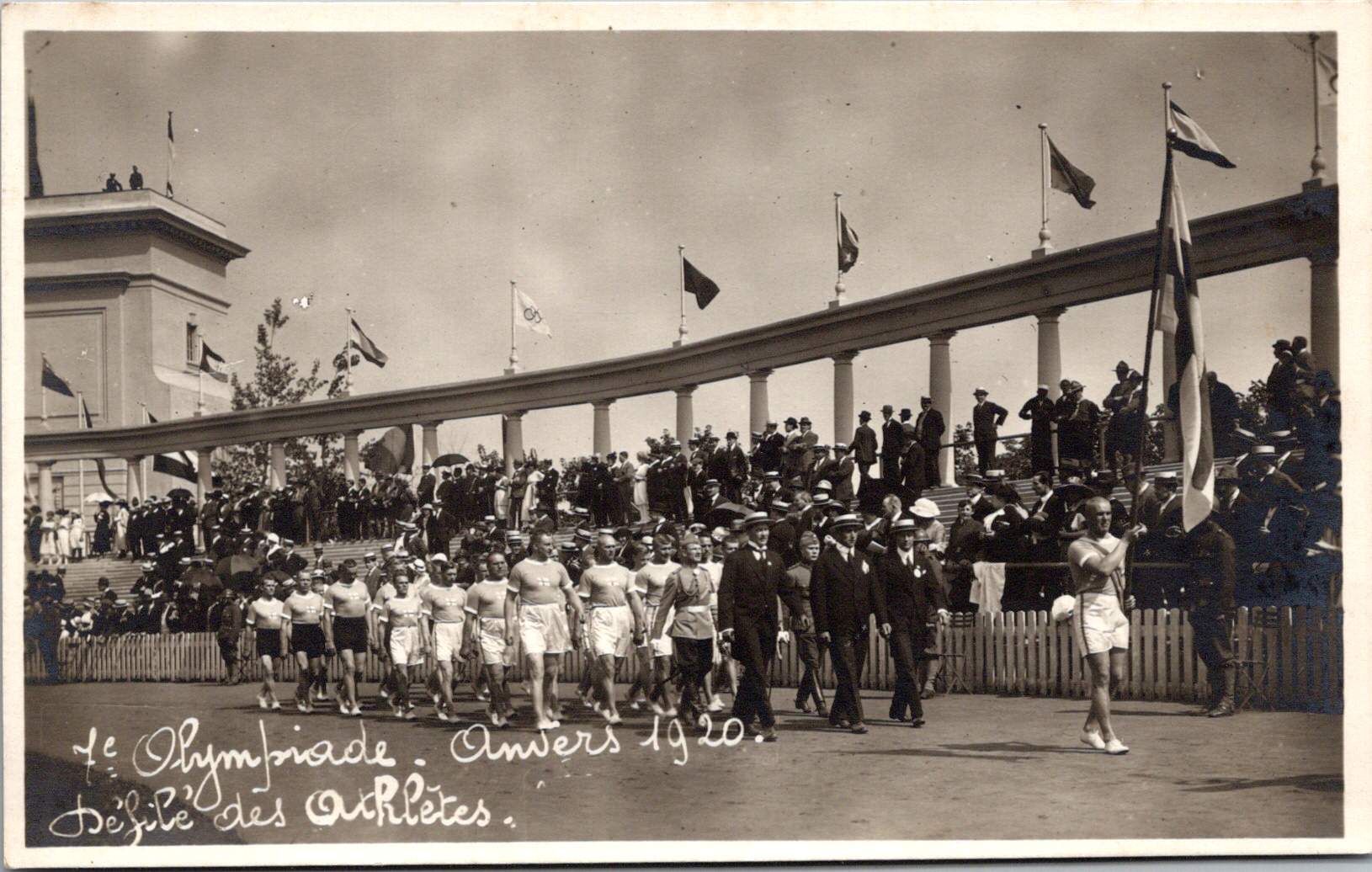






Man Behind the Mustache: Pierre de Coubertin
Baron Pierre de Coubertin is easily identified in the front row by his long and gray mustache. The visionary behind the revival of the Olympic Games must have felt pride and vindication at this moment. For de Coubertin, whose Olympic ideal centered on promoting international understanding and peace through sport, the successful staging of the Antwerp Games was nothing short of a triumph.
The 1920 Antwerp Olympics were the first Games held after the cancellation of the 1916 Olympics due to World War I. The year prior, the Inter-Allied Games were hosted in France, mostly to keep WWI troops occupied in the sudden transition out of war. The fact that de Coubertin stands alongside Pershing, a military leader, in this peaceful setting, perfectly encapsulates the Olympic dream of turning swords into javelins, conflict into friendly competition.
De Coubertin’s presence also connects the ancient Olympic tradition with the modern era. Under his direction, the iconic Olympic rings and flag were introduced in 1920, along with other modernizations in sport, gear, and rules of the games. There were limitations, too, especially related to the post-war economy. Top athletes went unchallenged in some categories when other countries could not afford to compete.
The choice of Antwerp as the host city was deeply significant. Belgium had suffered tremendously during World War I, with much of the country occupied and its people enduring great hardships. Hosting the Olympics was a statement of Belgium’s resilience and the international community’s support for its recovery. The stadium was more than just a sporting venue; it was a symbol of reconstruction and hope. Repurposed from the city’s hometown venue, it was transformed on short notice into the Olympisch Stadion.
The selection of Antwerp as host was not just a gesture of respect for the Olympic movement, but also an acknowledgment of Belgium’s sacrifices and its determination to rebuild. In the end, though, the city lost money on the Games due to low attendance.
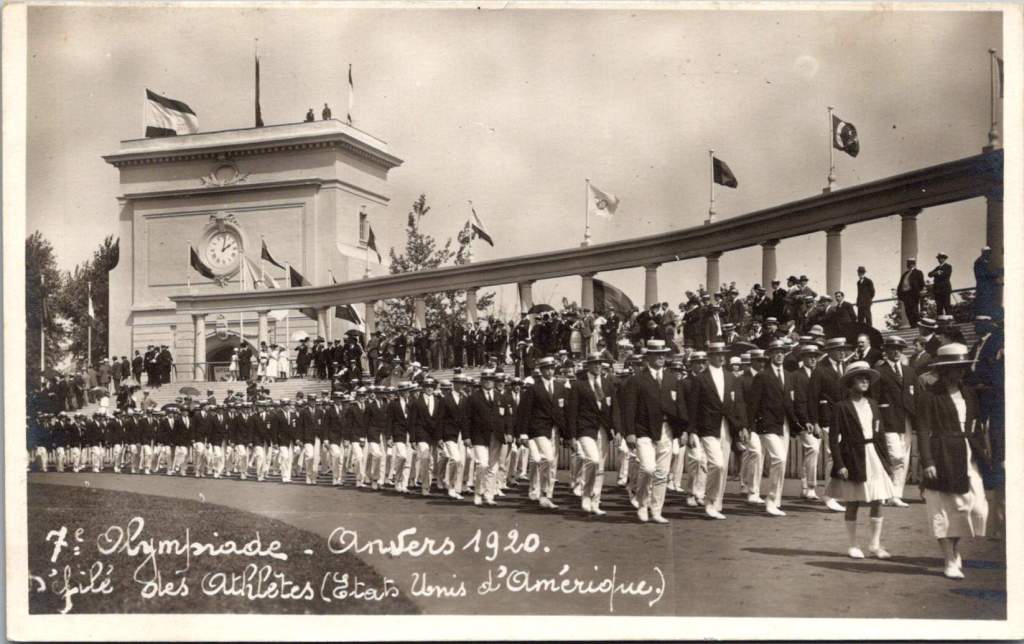
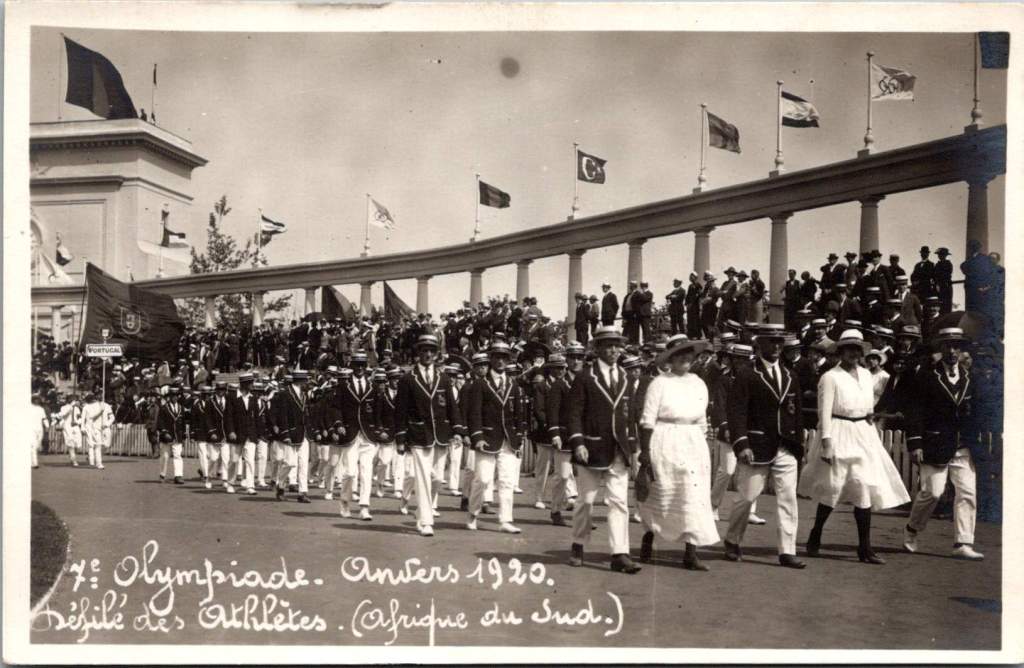





Photo Paper to Digital Pixels: The Evolution of Olympic Memories
As we examine this postcard set today, we’re struck by how much has changed in the way we capture and share moments of global significance. The photographer who snapped this image must have thought carefully about each shot, knowing that film and processing were expensive and opportunities fleeting.
Today, a similar scene would be captured by thousands of smartphone cameras, instantly shared across the globe. The modern Olympic Games are documented in minute detail, with high-definition video capturing every bead of sweat and every emotional reaction.
Yet, there’s something special about this centenarian postcard. Its physical nature, the silver halide crystals that hold the image fast, give it a permanence that our digital memories often lack. It’s a tangible connection to a pivotal moment in history, one that we can hold and examine closely. It’s also remarkably detailed, given the age and technology at hand.
In our era of information overload, where countless images flood our screens daily, the rarity of this postcard becomes even more significant. While we don’t know exactly how many of these postcards were produced – estimates range from several hundred to a few thousand – we know that most have been lost to time.
Each surviving postcard is now a valuable historical artifact. They appear occasionally at auctions, eagerly sought after by collectors who understand their significance. But beyond their monetary value, these postcards are treasure troves of historical information.
The T.I.C. logo and the small ‘x’ between POST and CARD on the back, for instance, tell us not just who made the paper, but in what year. This level of detail allows historians to verify the authenticity of Olympic memorabilia and build a more detailed understanding of how the games were documented.
Finding Our Photographer
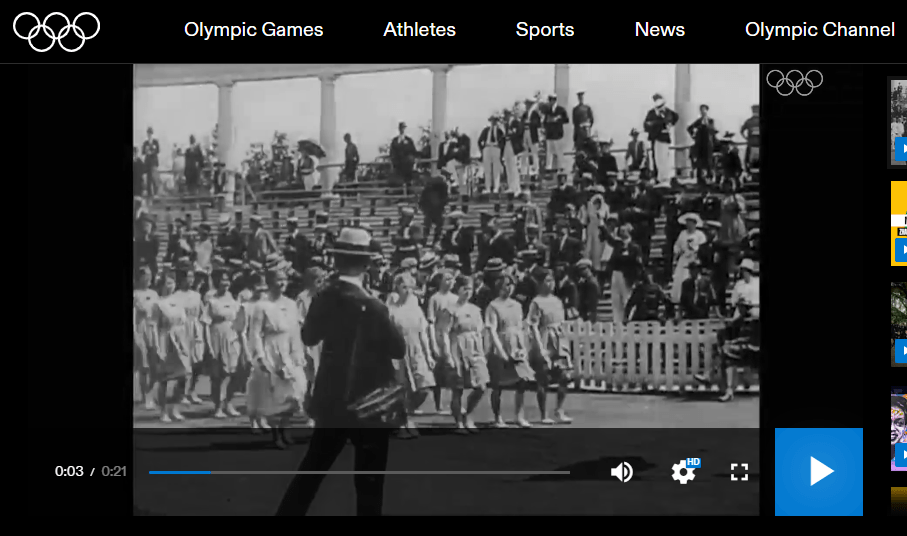
Who was the photographer? The mystery unraveled makes these rare images all the more interesting. Our research landed at the website for the official Olympic history, and a brief snippet of film from the 1920 opening ceremonies. In it we see a gaggle of photographers covering the proceedings. As the camera focuses, a sole figure breaks from the crowd and raises his camera for the perfect shot. The Denmark delegation is rounding the oval path and heading toward the risers. It’s the exact image we see in the postcard collection. Thrilling to have the photographic evidence, and travel through time to witness the moment!

Echoes Across Time
Seeing these images today, we can’t help but draw parallels between their time and ours. The world of 1920 was recovering from a pandemic and rebuilding after a major global conflict. The push for civil liberties was gaining strength in the U.S. and around the world. Today, we too are emerging from a global health crisis, facing international tensions, grappling with rapid technological change, and defending democracy.
The image of Pershing and de Coubertin, saluting the host country in an Olympic stadium, reminds us of the power of sport to bring people together. It shows us a world recovering after unimaginable hardship, finding unity in athletic achievement.
The Olympic Games continue to serve as a symbol of international cooperation and human achievement. As we look to the Olympics today, we might wonder: what form will our memories take? Will our digital images have the staying power of these centenarian postcards?
In an age where our memories are increasingly digital and ephemeral, these physical postcards serve as a poignant reminder of the value of tangible history. They urge us to consider how we document our own pivotal moments, and what legacy we will leave for future generations to discover. As we look to the future, may we carry forward the spirit of resilience, unity, and hope that these extraordinary images so powerfully illustrate.
Discover more from The Posted Past
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.

2 thoughts on “Precipice of Peace: Postcards from 1920 Antwerp Olympics”